Mortgage Rate Forecast: Rising Rates and Economic Resilience
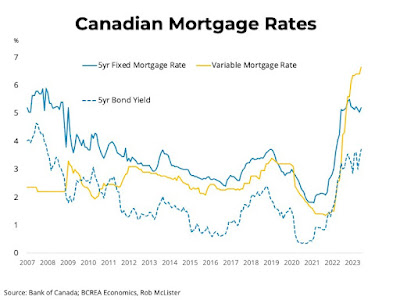
According to Brendon Ogmundson, the Chief Economist for the British Columbia Real Estate Association (BCREA), stubborn inflation has prompted a rise in mortgage rates. The Bank of Canada is anticipated to continue increasing rates in an effort to slow down the economy and bring inflation back to its target level. Following the release of April's inflation data, Canadian bond markets reacted by adjusting their expectations for monetary policy.
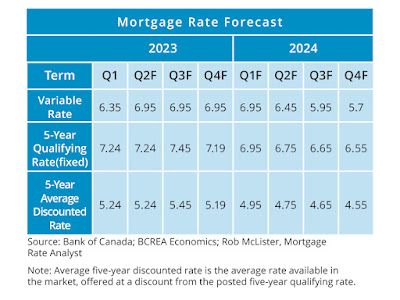
The yield curve in Canada remains significantly inverted, historically indicating the potential for recessionary conditions ahead. Despite the impact of higher interest rates, the economy has demonstrated resilience. However, it is expected that mortgage rates will continue to rise throughout the summer. The average five-year fixed mortgage rate is projected to remain above 5% for the year but may begin declining in the fourth quarter of 2023.
Variable rates are forecasted to reach 6.9% with the possibility of one more rate hike by the Bank of Canada in July. If the economy weakens as predicted and inflation shows signs of improvement, rate cuts by the central bank may be seen in early 2024. The Bank of Canada's objective is to bring inflation back to its 2% target through the implementation of higher interest rates.
The real policy rate, accounting for inflation, is anticipated to reach its highest level in over 15 years. As a consequence, the economy is expected to slow down, potentially leading to rate reductions by the Bank of Canada in 2024.


Comments
Post a Comment